Modern medicine is undergoing a significant technological revolution, with 3D printing taking a central role in this process. The use of this technology allows for the creation of customized medical devices, including prosthetics, implants, and even tissues. At Joy-pup, we will discuss the applications of 3D printing in medicine.
Prosthetics

One of the most striking examples of 3D printing is the production of prosthetics. Thanks to this technology, it is possible to create custom prosthetics that fit perfectly in shape and size to the patient. This significantly speeds up the adaptation process to new devices and reduces discomfort. 3D printing allows for the creation of prosthetics faster and cheaper than traditional methods.
Implants
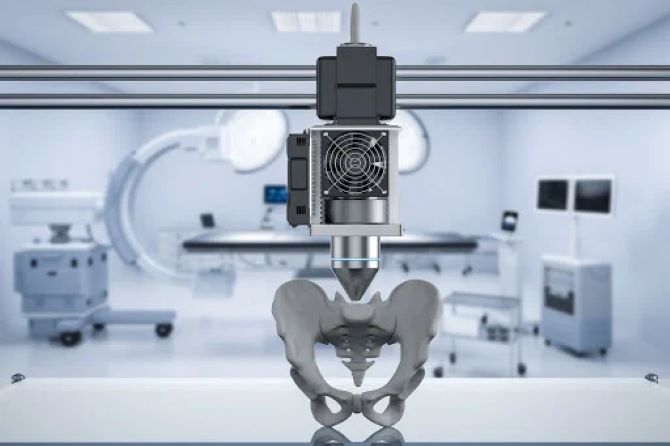
3D printing has also opened up opportunities for creating implants, such as bone or joint prosthetics. Unlike standard products, 3D-printed implants can be fully customized to the anatomical features of the specific patient. This increases the success rate of surgeries and speeds up rehabilitation.
Organic Tissues and Organs
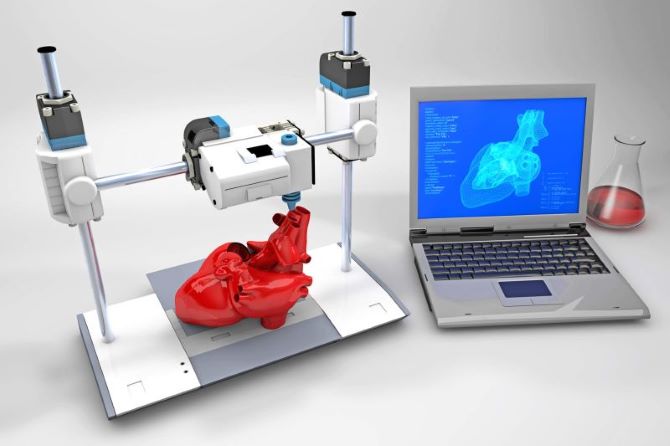
Although creating full organs for transplantation is still in the research stage, 3D printing is already actively used for printing organ models. These models help surgeons prepare for complex surgeries, significantly reducing the risk of complications. In the future, scientists aim to create functional organs that can replace donor transplants.
Medical Instruments
3D printing makes it possible to create unique medical instruments and devices that were previously difficult or expensive to manufacture. This allows medical institutions to quickly adapt to new needs and develop tools that meet the specific requirements of a procedure.






Only registered users can leave comments